Rgb To Munsell Converter Word
Munsell to CMYK Conversion (Long Shot) Pages: 1 2. I have a Munsell reference that I need to convert to CMYK. Does anyone know how to convert Munsell to CMYK (or an RGB colour space D65 illuminant)? Or possibly convert it for me if you have the tools. I can't find anything on the net that will allow me to do one conversion for free. I am rewriting an ASTM standard and am looking to identify a Pantone color chip that matches as closely as possible a specific Munsell color chip referenced in the current standard.
MUNSELL COLOR SYSTEM A perceptually uniform color space Developed in the early 20 th century by the American artist Albert H. Munsell (1858-1918), this is the first widely accepted color order system. It is traditionally presented as a collection of color patches known as the Munsell Book of Color. First devised as a color description teaching aid, the Munsell Color System was expanded and quantitatively formalized in the 1940s. The analysis led to small adjustments in the samples color in order to improve the spacing uniformity between them.
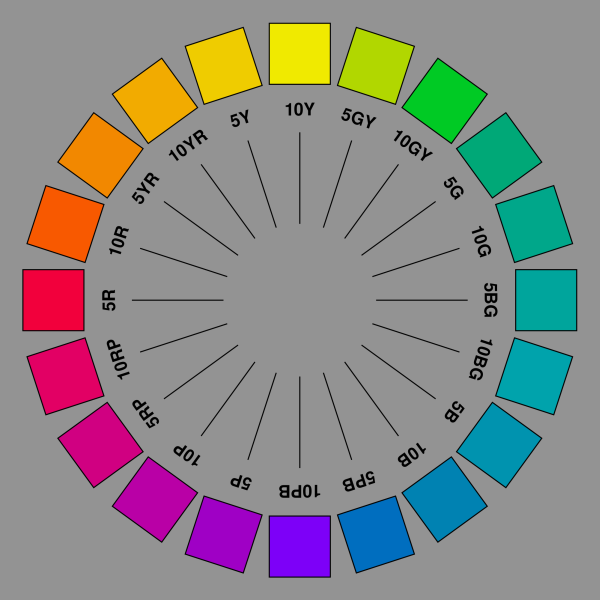
The results were published in 1943. The CIE coordinates of this “ renotated” system, as it is referred to, are the starting points from which the colors of the patches printed in this catalog were derived. The Munsell Color System is an international reference, defined in D1535 and other standards, that is used in many fields of work, from archaeology, when describing the colors of artifacts, to medical studies, when comparing the color of skin affections, to hobby activities such as accurately depicting the colors of scaled vintage airplanes. In this system, colors are identified with three parameters: Munsell Hue, Munsell Chroma and Munsell Value, or Munsell HVC for short; they are presented in the form “ Hue Value/ Chroma”. The Munsell Hues are separated in 10 hue ranges (please refer to the illustration above). Each hue range is identified by a major hue. The major hues are Red, Yellow, Green, Blue and Purple, as well as the five hues located between them and named by combining the names of the hues on each side.
For example, the hue located between Yellow and Red is called Yellow-Red, instead or Orange; this naming convention minimizes the number of color names one has to deal with. Each hue range is further divided in 10 sub-zones defined by 11 radii labeled from zero to 10. The hue with a “10” prefix at the end of a zone corresponds to the hue with a “0” prefix of the next zone.
For example, the 10Y hue is the same as 0GY; in practice the 10Y notation is the preferred one. The centers of each hue ranges are labeled 5R, 5YR, 5Y, 5GY, 5G, 5BG, 5B, 5PB, 5P, and 5RP.
The color circle is, in effect, separated in 100 hue segments where each hue separation is perceptually uniform. A zero to 100 number can be used to describe the Munsell Hue but it is seldom seen; the zero is at 10RP (or 0R) and the numbers increase when going counter- clockwise, up to 100, also at 10RP. The Munsell Book of Color typically has samples with hues located at every 2.5 hue steps. For example: 10RP (i.e. 0R), 2.5R, 5R, 7.5R and 10R for the red hue range. Neutral colors are presented in the form “ N 5/” with “N” written for the neutral hue, and no number for chroma since there is zero chroma. Fractional values are possible for each parameter, and “ 5.2R 4.8/17.5” is a valid Munsell notation.
The Munsell Chroma, like the C. of the L.C.h representation, can be considered an approximate counterpart of perceived color saturation, while the Munsell Value is associated to the lightness ( L.) of the color.
It is important to understand that the color system was not designed so that unitary steps of hue, value and chroma corresponded to identical color differences. However, the perceived chroma and value increase uniformly for similar steps of their respective scales. For instance, the perceived difference between Chroma 4 and Chroma 6 samples (i.e. /4 and /6) should be the same as the one perceived between Chroma 6 and Chroma 8 samples. Please note that while the Munsell space uniformity is high, it is not perfect, and will not necessarily hold in all viewing conditions, in particular with different background shades; this is discussed further below. According to the ASTM D1535 standard, the estimated precision with which a color can be characterized by visual interpolation is 0.5 hue step, 0.1 value step, and 0.4 chroma step. Maximum Munsell Chroma This illustration presents the patches of the 5R hue page of the BabelColor (not sold anymore), which is in the center of the Red hue range.
We can see that the sample with the highest Munsell Chroma is “ 5R 5/18”. In the catalog, the maximum chroma for a given Munsell Value depended on three factors. The first factor is inherent to the Munsell system. Munsell Chroma coordinates have no preset upper bound and large chroma values eventually represent colors which are outside the range of human-visible colors. The second factor is that chroma is limited by the color gamut of the printing system, which is a combination of the tint (i.e.
Web Color To Rgb Converter
Hue) and purity (i.e. Saturation) of the inks as they appear once printed on the selected paper. While colors outside of a printer profile’s gamut can be printed, the produced colors are generally highly inaccurate; these colors were identified and discarded. The third factor is a product design decision where it was decided to limit the maximum chroma to 18 (i.e. /18) for all pages.
This was done to maximize the patch size while keeping the same patch size and patch layout for all pages. A few patches were thus removed, in the RP hues for instance, in order to more completely fill the pages of other hues. Munsell Color System uniformity Munsell layouts sometimes appear non uniform in the low-chroma/high-value region. This may be partly due to the background on which the patches are compared, but it is also inherent to the system. Even if improved by the “renotation” efforts of the 1940s (see ), the Munsell system is not flawless. In fact, a committee, formed in 1947, worked for 30 years on a replacement color system called the Optical Society of America’s Uniform Color Scale ( OSA-UCS). While they could achieve a system with better uniformity than the Munsell system, they concluded that: “ no regular rhombohedral lattice sampling of color space, with a fixed background, can exist; we will produce the best approximation to such a lattice for a neutral 6/ background that we can design” In other words, the UCS system is more uniform, but only for one fixed background equivalent to Munsell N 6/.
The UCS structure offers unique multidirectional navigation paths in color space; unfortunately, it was not widely adopted, maybe because of its non-intuitive color notation format. Still, it remains useful, to this day, for color research.
It is then not surprising to see that work was done during the same period to improve the Munsell system, also by imposing a background. This work resulted in the development of Munsell “ re-renotation” tables , published in 1967, where it is assumed that “ two colors forming the difference are viewed on a gray background whose Munsell value approximates the average of the values of the two colors.” As for the UCS, we have not seen much use of these tables, and the “renotated” Munsell Color System published in 1943 remains a valid and trusted color reference. CIE and RGB coordinates of Munsell colors The CIE coordinates (XYZ, L.a.b., etc.) of over 4000 Munsell patches, including all the ones printed in the BabelColor Munsell Color System Catalog or the Munsell Book of Color, can be obtained with the program; these coordinates can be converted within the program to many or to a.
CT&A can also compute the Munsell equivalent of RGB and L.a.b. coordinates, or spectral measurements, with. PatchTool, another BabelColor program, can export any color data list opened in the program to. CT&A and PatchTool need to be purchased separately. Please consult the and documentation on this Web site for more information. 1: Final Report of the O.S.A.
Subcommittee on the Spacing of the Munsell Colors, Sidney M. Newhall, Dorothy Nickerson, and Deane B.
Judd, JOSA, Vol. 7, July 1943, p385-418. 2: o Uniform color scales, David L. MacAdam, JOSA, Vol. 12, December 1974, p1691-1702 o OSA Uniform Color Scale Samples: A Unique Set, Dorothy Nickerson, COLOR research and applications, Vol. 1, Spring 1981, p7-33 o On the Geometry of the OSA Uniform Color Scales Committee Space, Fred W.
Billmeyer Jr., COLOR research and applications, Vol. 1, Spring 1981, p34-37.
Ref. 3: One Set of Munsell Re-renotations, NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS REPORT #192693, Deane B. Judd and Dorothy Nickerson, December 26, 1967. MUNSELL COLOR SYSTEM A perceptually uniform color space Developed in the early 20 th century by the American artist Albert H. Munsell (1858-1918), this is the first widely accepted color order system. It is traditionally presented as a collection of color patches known as the Munsell Book of Color. First devised as a color description teaching aid, the Munsell Color System was expanded and quantitatively formalized in the 1940s.
The analysis led to small adjustments in the samples color in order to improve the spacing uniformity between them. The results were published in 1943. The CIE coordinates of this “ renotated” system, as it is referred to, are the starting points from which the colors of the patches printed in this catalog were derived. The Munsell Color System is an international reference, defined in D1535 and other standards, that is used in many fields of work, from archaeology, when describing the colors of artifacts, to medical studies, when comparing the color of skin affections, to hobby activities such as accurately depicting the colors of scaled vintage airplanes.
In this system, colors are identified with three parameters: Munsell Hue, Munsell Chroma and Munsell Value, or Munsell HVC for short; they are presented in the form “ Hue Value/ Chroma”. The Munsell Hues are separated in 10 hue ranges (please refer to the illustration above). Each hue range is identified by a major hue. The major hues are Red, Yellow, Green, Blue and Purple, as well as the five hues located between them and named by combining the names of the hues on each side. For example, the hue located between Yellow and Red is called Yellow-Red, instead or Orange; this naming convention minimizes the number of color names one has to deal with.
Munsell To Ral Converter
Each hue range is further divided in 10 sub-zones defined by 11 radii labeled from zero to 10. The hue with a “10” prefix at the end of a zone corresponds to the hue with a “0” prefix of the next zone. For example, the 10Y hue is the same as 0GY; in practice the 10Y notation is the preferred one. The centers of each hue ranges are labeled 5R, 5YR, 5Y, 5GY, 5G, 5BG, 5B, 5PB, 5P, and 5RP. The color circle is, in effect, separated in 100 hue segments where each hue separation is perceptually uniform. A zero to 100 number can be used to describe the Munsell Hue but it is seldom seen; the zero is at 10RP (or 0R) and the numbers increase when going counter- clockwise, up to 100, also at 10RP.
Rgb To Munsell Converter Word To Pdf
The Munsell Book of Color typically has samples with hues located at every 2.5 hue steps. For example: 10RP (i.e. 0R), 2.5R, 5R, 7.5R and 10R for the red hue range. Neutral colors are presented in the form “ N 5/” with “N” written for the neutral hue, and no number for chroma since there is zero chroma. Fractional values are possible for each parameter, and “ 5.2R 4.8/17.5” is a valid Munsell notation.
The Munsell Chroma, like the C. of the L.C.h representation, can be considered an approximate counterpart of perceived color saturation, while the Munsell Value is associated to the lightness ( L.) of the color. It is important to understand that the color system was not designed so that unitary steps of hue, value and chroma corresponded to identical color differences.
However, the perceived chroma and value increase uniformly for similar steps of their respective scales. For instance, the perceived difference between Chroma 4 and Chroma 6 samples (i.e. /4 and /6) should be the same as the one perceived between Chroma 6 and Chroma 8 samples. Please note that while the Munsell space uniformity is high, it is not perfect, and will not necessarily hold in all viewing conditions, in particular with different background shades; this is discussed further below. According to the ASTM D1535 standard, the estimated precision with which a color can be characterized by visual interpolation is 0.5 hue step, 0.1 value step, and 0.4 chroma step.
Maximum Munsell Chroma This illustration presents the patches of the 5R hue page of the BabelColor (not sold anymore), which is in the center of the Red hue range. We can see that the sample with the highest Munsell Chroma is “ 5R 5/18”. In the catalog, the maximum chroma for a given Munsell Value depended on three factors.

The first factor is inherent to the Munsell system. Munsell Chroma coordinates have no preset upper bound and large chroma values eventually represent colors which are outside the range of human-visible colors. The second factor is that chroma is limited by the color gamut of the printing system, which is a combination of the tint (i.e. Hue) and purity (i.e.
Saturation) of the inks as they appear once printed on the selected paper. While colors outside of a printer profile’s gamut can be printed, the produced colors are generally highly inaccurate; these colors were identified and discarded. The third factor is a product design decision where it was decided to limit the maximum chroma to 18 (i.e.
/18) for all pages. This was done to maximize the patch size while keeping the same patch size and patch layout for all pages. A few patches were thus removed, in the RP hues for instance, in order to more completely fill the pages of other hues. Munsell Color System uniformity Munsell layouts sometimes appear non uniform in the low-chroma/high-value region. This may be partly due to the background on which the patches are compared, but it is also inherent to the system. Even if improved by the “renotation” efforts of the 1940s (see ), the Munsell system is not flawless.
In fact, a committee, formed in 1947, worked for 30 years on a replacement color system called the Optical Society of America’s Uniform Color Scale ( OSA-UCS). While they could achieve a system with better uniformity than the Munsell system, they concluded that: “ no regular rhombohedral lattice sampling of color space, with a fixed background, can exist; we will produce the best approximation to such a lattice for a neutral 6/ background that we can design” In other words, the UCS system is more uniform, but only for one fixed background equivalent to Munsell N 6/. The UCS structure offers unique multidirectional navigation paths in color space; unfortunately, it was not widely adopted, maybe because of its non-intuitive color notation format. Still, it remains useful, to this day, for color research. It is then not surprising to see that work was done during the same period to improve the Munsell system, also by imposing a background.
This work resulted in the development of Munsell “ re-renotation” tables , published in 1967, where it is assumed that “ two colors forming the difference are viewed on a gray background whose Munsell value approximates the average of the values of the two colors.” As for the UCS, we have not seen much use of these tables, and the “renotated” Munsell Color System published in 1943 remains a valid and trusted color reference. CIE and RGB coordinates of Munsell colors The CIE coordinates (XYZ, L.a.b., etc.) of over 4000 Munsell patches, including all the ones printed in the BabelColor Munsell Color System Catalog or the Munsell Book of Color, can be obtained with the program; these coordinates can be converted within the program to many or to a. CT&A can also compute the Munsell equivalent of RGB and L.a.b. coordinates, or spectral measurements, with.
PatchTool, another BabelColor program, can export any color data list opened in the program to. CT&A and PatchTool need to be purchased separately. Please consult the and documentation on this Web site for more information.
1: Final Report of the O.S.A. Subcommittee on the Spacing of the Munsell Colors, Sidney M. Newhall, Dorothy Nickerson, and Deane B. Judd, JOSA, Vol. 7, July 1943, p385-418. 2: o Uniform color scales, David L. MacAdam, JOSA, Vol.
12, December 1974, p1691-1702 o OSA Uniform Color Scale Samples: A Unique Set, Dorothy Nickerson, COLOR research and applications, Vol. 1, Spring 1981, p7-33 o On the Geometry of the OSA Uniform Color Scales Committee Space, Fred W. Billmeyer Jr., COLOR research and applications, Vol. 1, Spring 1981, p34-37. Ref.
3: One Set of Munsell Re-renotations, NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS REPORT #192693, Deane B. Judd and Dorothy Nickerson, December 26, 1967.
Converting Colors RockWorks Utilities Grafix Color Converter This program is used to translate colors between a variety of different formats: RGB, Hexadecimal, Decimal (Windows 32-bit) integers, RockWare color names (from the ), and Munsell colors (from the Color Names table). Since RockWorks stores colors using the Decimal (Windows 32-bit) integer method, you can use the Color Converter program to determine the Windows integer value for any color in the color palette. This can be helpful if you are defining symbol colors, for example, in an Excel spreadsheet for import into the Borehole Manager, or for determining a Windows color for a known RGB sample. Step-by-Step Summary. Access the RockWorks Utilities program tab. Select the Grafix Color Converter menu option. Define the known color which you wish to translate.
(Enter only one of the possibilities.). Color Preview: Click on this button to browse for a color from the Windows color palette. RGB: Use these prompts to type in a known color in Red, Green, Blue values. Hexidecimal: Here you can type in a known hex color. Decimal (Windows 32-bit): Type in the Windows integer color here. Color Name: This prompt links to the alphanumeric RockWorks Color Names table, specifically to the grouping ('System Number') #1.
These are descriptive words like 'Brown'. (If you import/add your own color names to this table, you'll probably want to add them to the #1 grouping so they'd be accessible from this program.). Munsell (Hue/Value/Chroma): This prompt also links to the Color Names table, to grouping #2 where geo-specific Munsell codes have been entered. When you're ready to translate the known color, entered into one of the options listed above, to all of the others, click the green arrow button. The program will translate the color to the other formats and display them next to the prompts. Note that for the Color Name and Munsell options, the closest possible color will be displayed.
In addition, the programwill copy the currently selected Windows 32-bit color number to the Windows clipboard so that selected colors can be copied back to other applications. (In other words, we figure that you're using this program to look up a color for some other RockWorks application.) Back to.